Technology Development
Developing equitable, sustainable and scalable technology to ensure no one is left behind.EWB is uniquely positioned as an independent entity to facilitate the development of solutions for social change through cross-sectoral collaborations between community partners, corporate engineering firms, academic institutions, other organisations and enterprises alongside EWB’s volunteer movement.
EWB engages in technology development through three key mechanisms
- Leading the development of bespoke, place-based and community-driven technologies
- Leading the development of low-cost, decentralized technologies (products)
- Consulting to vision-aligned organisations in support of technology development projects
EWB acts not only as a broker between organisations and individuals, but also actively leads engineering and product development projects, leveraging input from a wider network as well as the capability of EWB staff and volunteer movement around Australia and the Asia-Pacific.
EWB Australia’s Technology Development team is currently focused on assistive technology, to support people with disabilities access agriculture linked livelihoods in Cambodia and Indonesia.
How EWB is unique
EWB brings together five essential pillars, which are rarely combined, yet are essential to deliver long-term, sustainable, appropriate and scalable solutions.

- Effective community engagement, support and management
- Technical expertise in using participatory approaches for technology development, through human-centred and co-design processes
- Technical expertise in product design, mechanical engineering and manufacturing
- Experience managing product development processes from concept development through to design for manufacture (DFM)
- Experience in setting up and managing manufacturing systems and sustainable supply chains
Our Approach
Our Human-Centred Engineering approach is uniquely designed to guide the development and implementation of equitable, sustainable and scalable solutions. It is underpinned by a diverse knowledge base, a robust set of guiding principles and framed around a formal technology development process. At different stages of the process, a series of tools and techniques are used to support project activities and meet specific outcomes.
Knowledge Base
Three distinct knowledge-sets are required for effective project work to occur:
Process knowledge
understanding of the required design steps, high-level tools and techniques and a mind-set conducive with design work
Contextual knowledge
general understanding of a range of topics focused on the socio-contextual environment in which the project is based.
Technical knowledge
in-depth understanding of technical areas, concepts, tools and techniques as well as existing solutions
Guiding Principles
Human-Centred Engineering balances socio-cultural, technical and environmental considerations to deliver impactful technology solutions. This work is underpinned by ten guiding principles, relevant to all projects undertaken:
- Prioritize community-identified needs
- Prioritize the inclusion of all
- Prioritize immersive and interpersonal experiences
- Do no harm
- Practice a strengths-based approach
- Practice systems-thinking
- Practice iterative design
- Encourage and manage ambiguity
- Encourage collaboration and mutual learning
- Focus on impact, not technology
Technology Development Process
EWB Australia has developed a design process to specifically guide engineering projects that aim to develop impactful solutions in challenging environments. This is complemented by a parallel design process that looks at implementation mechanisms required to support the sustainable scale of technologies.
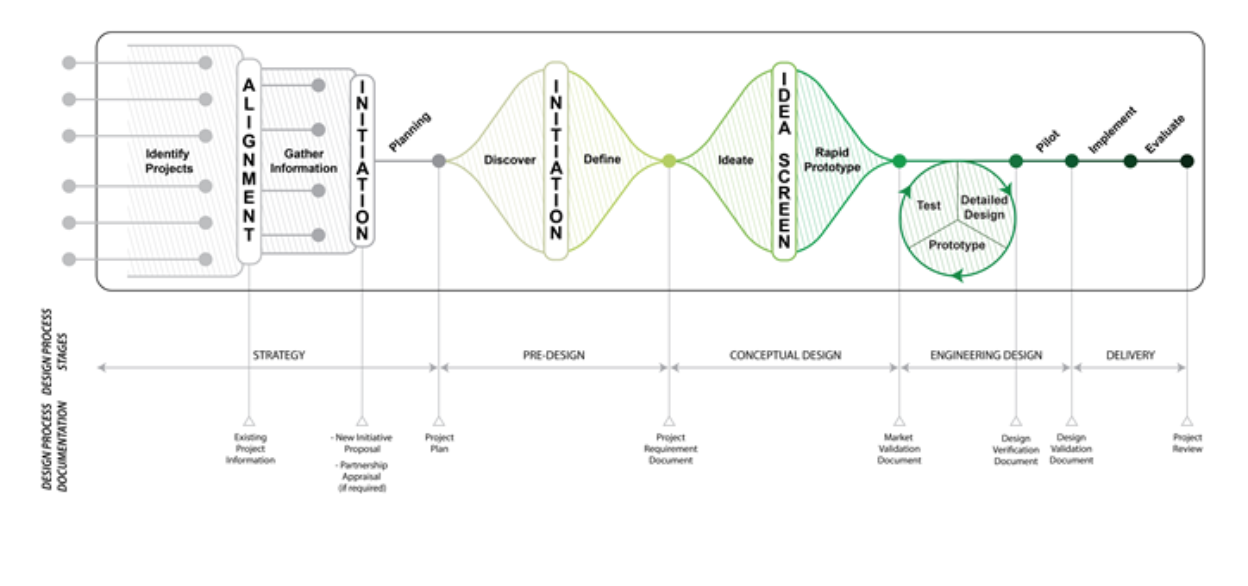
Tools and Techniques
EWB Australia utilises a range of tools and techniques to support achieving the required outcomes during process:
1. Contextual Learning
Gaining insights (strengths, challenges, existing projects, etc.) about the geo-socio-cultural environment, the community and the specific individuals impacted.
2. Creativity
Encouraging divergent, creative thinking that can lead to new, innovative ideas for solutions that address the identified project requirements.
3. Human Factors
Universal and culturally-specific psychological/physiological characteristics of individuals and communities that can support effective project implementation.
4. Systems Thinking
Understanding the geo-socio-cultural environment, ecological impact, inter-dependency and managing complexity.
5. Strategic Visioning
Identifying desirable future-states for a geo-socio-cultural environment, community or specific individual.
6. Technical Tools
Technical domain-specific requirements (e.g. WASH, medical device design) to ensure a technically effective and safe solution.
Support a Project
Many of our projects seek support – either through funding or pro-bono/volunteering services. Keen to help us make these projects come to life? Express your interest below, and we’ll be in touch.

